-
The mempool is a data structure which lists all transactions that were validated by the nodes but unconfirmed by the blockchain.
-
If the mempool becomes too congested, longer wait times will result. It may even get to the point where they get rid of the lowest fee transactions and replace them with the higher fee transaction
-
A growing mempool will increase transaction fees.
-
A list of unconfirmed tx’s on a node, waiting to be confirmed by a miner who puts the tx’s on the blockchain (=confirms the tx’s)
-
The mempool gets bigger and it will take longer to confirm the tx.
-
It will increase the tx fees, so it will be chosen earlier by the miners. Because miners first choice are the tx’s with the highest fees.
What is a mempool?
it is a pool of unconfirmed transaction.
What happens if the miners can’t keep u p with the rate of the new transaction?
The mempool will grow and that makes that the transaction will take longer before it is processed.
How does a growing mempool effect transaction fees?
Transaction fees will get higher so the miners will pick this transaction faster. ( compition between miners.
- It’s all the unconfirmed transactions that make sense stored on the nodes memory.
- If miners can’t keep up with the transactions, the mempool grows.
- Growing mempool makes transactions fees rise because it is taking up too much room on the block.
-
It is the waiting area for unconfirmed transactions waiting to be added onto blocks. Once a transaction is signed and broadcasted onto the network it goes to the mempool, from which miners take groups of transactions to build blocks in the network.
-
The mempool will grow and so the waiting time for transactions to be added onto blocks and be confirmed.
-
Transaction fees will grow. The transaction offering the highest fee per memory space used in the block will always be taken first to be added onto the block being built. This price per memory space is obviously calculated in satoshis per byte.
1.What is the mempool?
The mempool is a list of unconfirmed transactions waiting to be processed.
2.What happens if the miners can’t keep up with the rate of the new transaction?
New transactions that are not able to be processed will sit in the mempool, and then get picked up by miners based on transaction fee. Miners will prioritise the transactions with the highest fee.
3.How does a growing mempool affect transaction fees?
As the mempool fills with transactions, there is more competition. This means fees rise as miner demand increases.
- What is the mempool?
A queryable log of all yet to be confirmed transactions. - What happens if the miners can’t keep up with the rate of the new transaction?
the network begins to experience congestion, which means longer transaction verification wait times. - How does a growing mempool effect transaction fees?
Because transactions with a higher fees will be prioritized, the suggested fee per transaction will be increased in order to ensure transaction validation. Naturally, some will opt to pay more for their transaction than others (gas wars).
1. What is the mempool?
The mempool (memory pool) is a small database of unconfirmed and pending transactions. Here they are waiting for a miner to pick them up and add to the next block.
2. What happens if the miners can’t keep up with the rate of the new transaction?
The mempool piles up with those pending transactions, and the time of confirmation them will be longer.
Transactions with higher fees will be be priorititized by the nodes/miners and the transaction costs will rise.
3. How does a growing mempool effect transaction fees?
The nodes/miners will prioritize the higher fee transactions and this will result in that transactions pile up in the mempool and fees go up.
People will have to pay higher fees to get their transactions picked up and processed faster.
- mempool is the place where unconfirmed transactions go and wait to be added to a block by the miners
- the mempool will grow in size if the miners cant keep up
- miners will pick the transactions with higher fees first; people may have to pay more in order to get the transaction processed and added to the block
- What is the mempool?
This is the storage area for unconfirmed transactions on a node.
- What happens if the miners can’t keep up with the rate of the new transaction?
The mempool grows. The transactions with the higher transaction costs are favored.
- How does a growing mempool effect transaction fees?
Proportionally, as the number of unconfirmed transactions increases, the amount of expensive transactions that are preferred also increases.
-
a mempool is a list of uncomfired transactions kept by nodes
-
mempools grow larger and transaction time increase as well as transaction fees.
-
a growing mempool would increase the fees for transactions. As there is more demand for transactions people would be more leniant towards higher transaction fees to make their transaction complete.
Mempool (short for memory pool) is an intermediate memory space that temporarily stores transactions before they are confirmed and permanently written into the blockchain. Since the blockchain can only write a limited number of transactions and blocks on any unit of time, the mempool is a necessary component of the blockchain protocol that allows to temporarily receive and put on hold an arbitrary number of transaction requests happening at any moment.
A typical user of Bitcoin does not interact directly with the mempool, and in fact may not even know there is something called the mempool. However, anyone who has regularly used the bitcoin network for a few months has experienced that there are moments when network fees are high and moments when network fees are low, and has an intuition that this is related to network congestion. Understanding how the mempool works and using online services like mempool.space can be very useful:
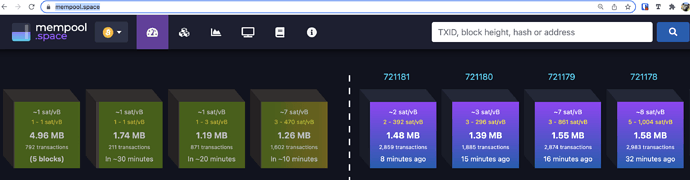
The blue cubes that you see on the right symbolize all past blocks already stored in the blockchain (a consensus has been reached). They are numbered 721181, 721180, … all the way until the first transaction. The green cubes on the left are waiting in the queue and hopefully they will eventually make it to the right list. The space where all these green cubes are stored is the actual mempool.
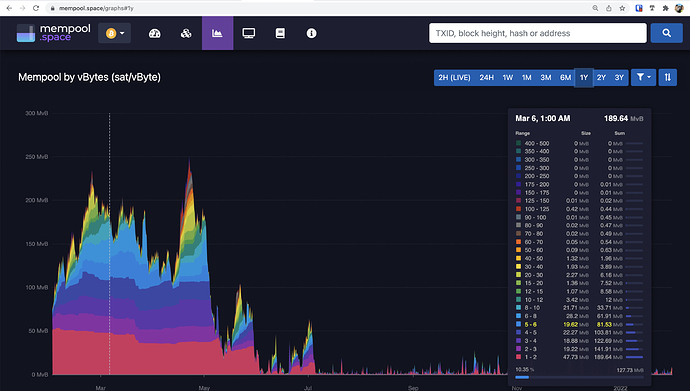
In order to quantify how big the mempool is, services like mempool.space provide graphics. On the X-axis you have time, and on the Y-axis you have a measurement of the Mempool size in satoshis/vBytes (a measurement of the BTC fee cost for each new confirmed block).
In layman terms, the higher the Mempool size at a specific point in time, the more expensive it is to make a transaction. Transaction fee hikes can happen either because there is an increase in the network activity (which in turn may be because something fishy is going on in the markets), or because the network has some technical problem, or a combination of both.
-
The mempool size will increase. More unconfirmed blocks will be waiting.
-
Fees will increase because of supply/demand. You will need to pay more in order for your transaction to be accepted into the next block.
- Mempool is the collection of unconfimed transactions stored in a node.
- The mempool will increase with more unconfirmed transactions.
- Miners will pick the transactions with the higher fees, so it means higher fees for those who want confirmation faster.
-
What is the mempool?
A place where transactions are stored before they get verified -
What happens if the miners can’t keep up with the rate of the new transaction?
The mempool gets bigger -
How does a growing mempool effect transaction fees?
They go up
-
All unconfirmed transactions being stored on a node.
-
The mempool will grow and thus the waiting time for new transactions to be verified increases.
-
Transaction fees increase since more transactions need to be verified.
It is the collection of validated transactions stored by a node.
The mempool keeps increasing, which brings more miners in due to the reasons listed below.
A growing mempool means higher transaction fees, which means a better incentive to mine. More miners looking to make money results in transaction fees falling again (it’s cyclical in a way).
- The place in node, where unconfirmed transactions are stored.
- Transaction time increases.
- The fee increases.
- a bucket of unconfirmed transactions
- the mempool increases
- it increases transaction fees
-
A list of un confirmed transactions
-
They prioritize each transaction that will pay more.
-
A growing amount of transactions means the fees will be higher for those that want to have there
Transactions confirmed.
- This is a place where unconfirmed transactions are kept until they are added to the block by miner.
- Transaction will take a longer time.
- Fees will be increased.