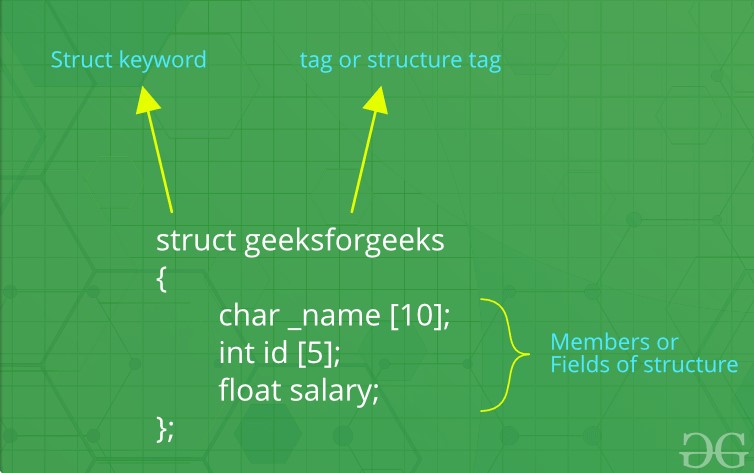
- it allows us to categorize variables of mix data types together into a single unit.
- the different variables the make up a struct
- a period aka the member selection operator
- structs inside another struct
-
Structs are useful because we can present multiple variables (properties) in one object.
-
Members are the properties of the struct.
-
To access the member inside a struct, we use the member selection operator (period).
-
A nested struct is having struct inside another struct. In other words, one of the members of a struct could be a struct.
- Structs give programmers the ability to group mixed-data type variables together in a single unit, making them far more efficient than repeatedly declaring mixed data-type variables repeatedly for multiple objects
- Members are the variables which are part of structs. They can be of different data types.
- Members inside structs are accessed via the member selection operator (represented by a period).
- Nested structs are structs within structs. They can be initialized using nested initializers
- It allows us to group variables of mixed data types together into a single unit.
- Variables that are part of the struct.
- We use a member selection operator or a period.
- Structs thatcontains other structs.
-
It is used to group values together.
-
Individual variables.
-
struct.member
-
A struct within another struct.
1. Why do we need structs?
Grouping variables to better represent real world objects.
2. What are members in a struct?
Members are the several variables of a struct
3. How do you access a member inside a struct?
struct.member
4. What is a nested struct?
It’s a struct inside a struct.
- Why do we need structs?
- What are members in a struct?
- How do you access a member inside a struct?
- What is a nested struct?
1: we need them to save numerous elements of different types in a single variable.
2: members in structs are the same as elements in arrays(variables).
3: with the dot operator: struct name. element=15;
4: a struct operating within another struct.
Why do we need structs?
It groups variables of mixed data types together into a single unit.
What are members in a struct?
The members are variables that are part of the struct. They are also named Fields.
How do you access a member inside a struct?
You use the member selection operator also known as a period.
What is a nested struct?
Basically, a struct within a struct.
1. Why do we need structs?
-
Structs are a simple way to define our own user-defined aggregate datatypes and there are many instances where we need more than one variable in order to represent an object.
-
Structs allow us to group variables of mixed data types together into a single unit.
2. What are members in a struct?
- The variables that are part of the struct are called members (or fields). These variables are a part of the struct declaration, but no memory is allocated at this time.
struct Student {
// members:
string name;
int age;
string gender;
};
3. How do you access a member inside a struct?
-
In order to access the individual members of a struct, we use the member selection operator (which is a period) to initialize each member variable.
-
Create a Student struct for a student
-
Initialize variables manually using dot notation and assign a value to member variables within the struct.
Student cian;
cian.name = "Cian";
cian.age = 33;
cian.gender = "female";
4. What is a nested struct?
- When a structure contains another structure. Structs can contain other structs.
- Structs are required to group variables of mixed data types together into a single unit.
- Members are defined variables inside of the struct.
- Accessing a member inside a struct is done using the member selector operator (struct.variable)
- A nested struct is a struct that resides within another struct. ie: struct.struct.variable
Q: Why do we need structs?
A: Because it helps us group variables of mixed data in a unit.
Q: What are members in a struct?
A: Variables that are part of a struct. For example, in
struct Object {
string name
double width
double length
double height
int previousOwners
}; // In this struct strings, doubles, and integers are called members of the struct.
Q: How do you access a member inside a struct?
A: We define a variable and then we can access the members. For example:
Object table;
table.name = “Table”;
table.width = 70.2;
table.length = 100.5;
table.height = 35.7;
table.previousOwners = 3;
Q: What is a nested struct?
A: A struct inside a struct.
[quote=“ivan, post:1, topic:3169”]
-
Why do we need structs?
When we need more than one variable to represent an object. -
What are members in a struct?
The variable that are part of the struct.
-
How do you access a member inside a struct?
In order to access the individual members, we use the member selection operator (which is a period). -
What is a nested struct?
Structs that contain other structs.
1: So we can create our own datatypes for variables that are objects.
2: Members are considered the variables of the Struct itself.
3:struct.member
4: A nested struct, is a Struct, inside of another struct.
-
Why do we need structs? Structs make it easier to create and manage variables of different data types together into one unit.
-
What are members in a struct? The variable that make up the struct.
-
How do you access a member inside a struct? Using the struct name followed by “.” and member id. Ex struct Person a ge; Person joe; (joe.age;)
-
What is a nested struct? Struct with a struct.
-
Why do we need structs?
To describe objects with multiple atributes all bundled together within a single variable. -
What are members in a struct?
The variables in the struct -
How do you access a member inside a struct?
using a member selection operator. Example Struct.member -
What is a nested struct?
A nested struct is a struct inside other struct
-
We need Structs becuase there are instances in programming where we need more than one variable in order to represent an object. A struct (short for structure) allows us to group variables of mixed data types together into a single unit.
-
Members are variables contained inside the Struct.
-
In order to access the individual members, we use the member selection operator (which is a period).
-
A nested struct is a struct inside of a struct.
- Why do we need structs? A struct (short for structure) allows us to group variables of mixed data types together into a single unit.
- What are members in a struct? variables that are part of the struct are called members (or fields)
- ***How do you access a member inside a struct?***struct.member
- ***What is a nested struct?***struct within a struct
- Structs allow us to group variables of mixed data types within a single unit.
- Members are the variables in the struct, also called fields.
- You use the member selection operator (period symbol) to access members in a struct. E.g., “person.ivan”
- A nested struct is a struct within a struct.
Why do we need structs?
To use more than one variable for the represenatation of an object.
What are members in a struct?
All variables inside the struct are members of the struct
How do you access a member inside a struct?
You need an alias as explained in the tutorial Person p
As example
void printPersonInfo (Person p) {
cout << "The name is: " << p.name << endl ;
cout << "The age is: " << p.age << endl ;
cout << "The gender is: " << p.gender<< endl ;
}
What is a nested struct?
It is a struct in a struct. Like the russian puppet called Matryoshka doll 
-
We need it to aggregate data types into single units that would, otherwise, take too many individual variables.
-
Members (or fields) are the variables that are part of the struct.
-
By using/creating the member selection operator, manually initializing struct variables.
-
It is a struct that contains other structs, using nested initializer lists for nested structs.