-
What is a digital certificate?
A digital certificate, also known as a public key certificate , is used to cryptographically link ownership of a public key with the entity that owns it. Digital certificates are for sharing public keys to be used for encryption and authentication. -
What is the difference between a digital certificate and a public key?
A certificate defines the ownership and a public key validates the ownership -
What is the most common use case for digital certificates?
To assure a secure connection between the web server and the browser. And they are also used for signing and encryption -
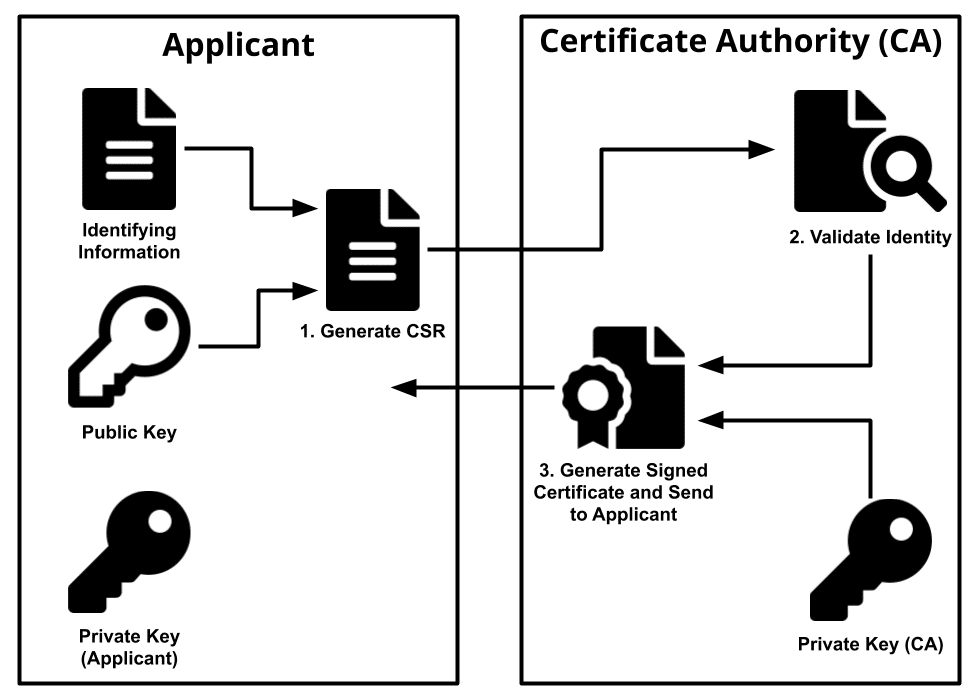
What is a certificate authority?
Its a trusted third party that issues digital certificates
-
- A digital certificate is used to cryptographically link ownership of a public key with the entity that owns it.
2)In public key cryptography; digital signatures are generated using algorithms for signing of data, with the result that a recipient can irrefutably confirm that the data was signed by the holder of a particular public key. Whereas digital certificates themselves are signed digitally, they should not be trusted unless the signature can be verified.
3)to retrieve the public key of and information about an entity and verify the ownership. This implies functionality of a public/private key pair
4)It is a trusted third party that issues digital certificates in the PKI context.
- A digital certificate is used to cryptographically link ownership of a public key with the entity that owns it.
-
What is a digital certificate?
Is also known as a public key certificate, is used to cryptographically link ownership of a public key with the entity that owns it. -
What is the difference between a digital certificate and a public key?
Digital certificates include the public key being certified, identifying information about the entity that owns the public key.
Public key cryptography depends on key pairs: one [private key] to be held by the owner and used for signing and decrypting and one public key that can be used for encrypting data sent to the public key owner or authenticating the certificate holder’s signed data.
- What is the most common use case for digital certificates?
-
Websites use digital certificates for domain validation to show they are trusted and authentic.
-
Digital certificates are used in secure email to identify one user to another and may also be used for electronic document signing. The sender digitally signs the email, and the recipient verifies the signature.
- What is a certificate authority?
Considered trusted third parties in the context of a PKI – issue most digital certificates. Using a trusted third party to issue digital certificates enables individuals to extend their trust in the CA to the digital certificates it issues.
-
What is a digital certificate?
A digital certificate is used to cryptographically link ownership of a public key with the entity that owns it. Digital certificates are for sharing public keys to be used for encryption and authentication. -
What is the difference between a digital certificate and a public key?
Public key cryptography depends on key pairs: one (private key) to be held by the owner and used for signing and decrypting and one public key that can be used for encrypting data sent to the public key owner or authenticating the certificate holder’s signed data. The digital certificate enables entities to share their public key so it can be authenticated. -
What is the most common use case for digital certificates?
Digital certificates are used in public key cryptography functions most commonly for initializing Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) connections between web browsers and web servers. Digital certificates are also used for sharing keys used for public key encryption and authentication of digital signatures. -
What is a certificate authority?
Certificate authorities [CAs] – considered trusted third parties in the context of a PKI – issue most digital certificates. Using a trusted third party to issue digital certificates enables individuals to extend their trust in the CA to the digital certificates it issues.
- What is a digital certificate?
Is a ownership digital proof, it uses cryptography. - What is the difference between a digital certificate and a public key?
Is the digital certificate that ensures the ownership while the public keys the encryption. - What is the most common use case for digital certificates?
SSL connections between browsers and servers, it shares keys used for public key encryption and authentication of digital signatures. - What is a certificate authority?
Is an entity that issues SSL certificates. These digital certificates are data files that links an entity with a public key. Web browsers use them to authenticate and verify content sent from web servers, delivering trust in content online.
1) What is a digital certificate?
- A digital certificate, which is known a public key certificate as well, is used to cryptographically link the ownership of a public key to the entity that owns it. Digital certificates purpose is for sharing public keys for encryption and authentication.
2) What is the difference between a digital certificate and a public key?
- The digital certificate include the public key being certified, identifying information about the entity that holds that specific public key, metadata related to the digital certificate and a digital signature of the public key that the issuer created.
- The public key itself is part of the digital certificate and has two main functions:
- Encrypting data sent to the public key owner;
- Authenticating the certificate’s holder signed data.
3) What is the most common use case for digital certificates?
- The most common case of use for digital certifications is for initializing secure SSL connections between the clients (web browser) and web servers. Digital certificates are used also for sharing keys that are used for public key encryption and for authentication of digital signatures.
4) What is a certificate authority?
- Certificate Authority (CAs) are third-parties that are trusted in the context of a PKI (Public Key Infrastructure). They are the ones who normally issue the digital certificates.
-
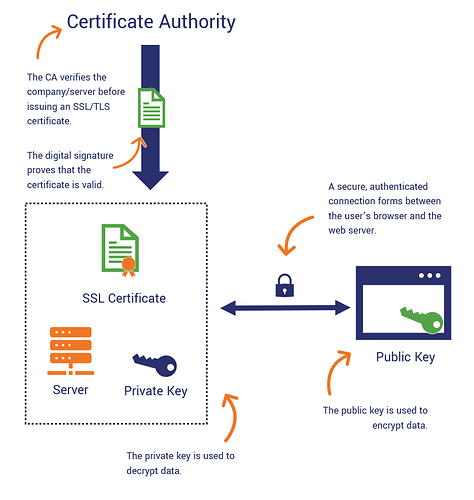
A digital certificate is also known as a public key certificate , it is used to cryptographically link ownership of a public key with the entity that owns it. Digital certificates are for sharing public keys to be used for encryption and authentication. Digital certificates include the public key, identity information about the owner and the name of the issuing certificate authority.
-
The difference between a digital certificate and a public key is that only the owner can access the private key to decrypt messages that are encrypted with corresponding public key. Signed digital certificate is an industry standard method of verifying the authenticity of an entity, such are a server, a client or an application. The digital certificate enables entities to share their public key so it can be authenticated. Digital certificates include the public key being certified, identifying information about the entity that owns the public key.
-
Digital certificates are authenticating the identity and providing secure electronic communication and data exchange between people, systems and devices online. Most commonly they been used in public web servers and internet facing servers, to secure websites, web servers, devices connected to web, any sort of code, software, signatures, also used in the email, HTTPS, FTPS,`WebDAV. Digital Certificates prove that websites and genuine and users are legitimates.
-
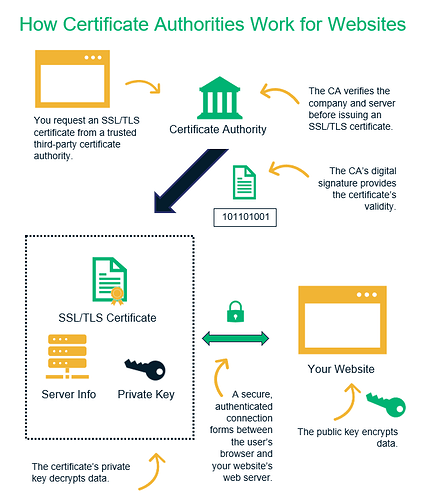
Certificate Authority is issuer of Digital Certificates they are verifying the identity of sender or receiver of an electronic message, considered trusted third party. In cryptography Certificate Authority is an entity that stores, signs and issues digital certificates which certifies the ownership of a public key.
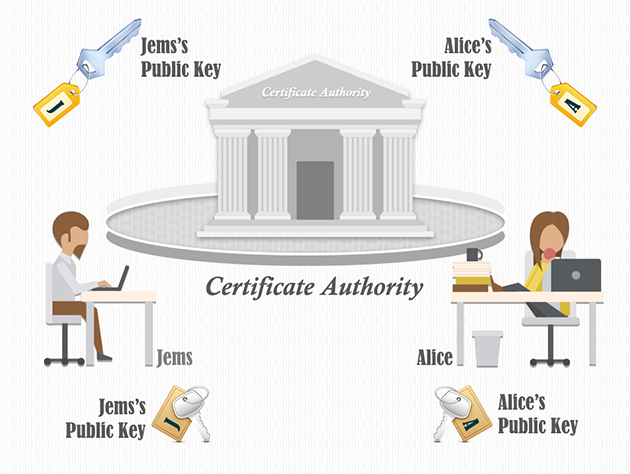
- A certificate that cryptographically links a public key to the entity that owns it
- A digital certificate includes the public key as well as other information
- initializing Secure Socket Layer connections
- Trusted third parties that issue digital certificates
1. What is a digital certificate?
A digital certificate, also known as a public key certificate , is used to cryptographically link ownership of a public key with the entity that owns it. Digital certificates are for sharing public keys to be used for encryption and authentication.
Digital certificates include the public key being certified, identifying information about the entity that owns the public key, metadata relating to the digital certificate and a digital signature of the public key the certificate issuer created.
2. What is the difference between a digital certificate and a public key?
Public key cryptography depends on key pairs: one private key to be held by the owner and used for signing and decrypting and one public key that can be used for encrypting data sent to the public key owner or authenticating the certificate holder’s signed data. The digital certificate enables entities to share their public key so it can be authenticated.
3. What is the most common use case for digital certificates?
Digital certificates are used in public key cryptography functions most commonly for initializing Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) connections between web browsers and web servers. Digital certificates are also used for sharing keys used for public key encryption and authentication of digital signatures.
Digital certificates are also used in other contexts, online and offline, for providing cryptographic assurance and data privacy.
• Credit and debit cards use chip-embedded digital certificates that connect with merchants and banks to ensure that the transactions performed are secure and authentic.
• Digital payment companies use digital certificates to authenticate their automated teller machines, kiosks and point-of-sale equipment in the field with a central server in their data center.
• Websites use digital certificates for domain validation to show they are trusted and authentic.
• Digital certificates are used in secure email to identify one user to another and may also be used for electronic document signing. The sender digitally signs the email, and the recipient verifies the signature.
• Computer hardware manufacturers embed digital certificates into cable modems to help prevent the theft of broadband service through device cloning.
4. What is a certificate authority?
Trusted third parties in the context of a. public key infrastructure (PKI), - issue most digital certificates. Using a trusted third party to issue digital certificates enables individuals to extend their trust in the Certificate Authorities (CA) to the digital certificates it issues.
1.) What is a digital certificate?
They are a record that has the following elements: a pubic key to be certified, identifying information about the entity that owns the public key, metadata relating to the digital certificate, and the digital signature of the public key the certificate issuer created. They are used to link a private key publicly to an identity that is known to the system.
2.) What is the difference between a digital certificate and a public key?
A digital certificate is an ownership record of a public key. It includes a signature of the public key by the private key.
3.) What is the most common use case for digital certificates?
The most common use case for certificates are initializing secure SSL connections between web browsers and web services.
4.) What is a certificate authority?
A certificate authority is a trusted party within the system with the authority to issue public keys. All digital certificates derive from the certificate authority’s system-wide trust.
-
Is used to cryptographically link ownership of a public key with the entity that owns it. Digital certificates are for sharing public keys to be used for encryption and authentication.
-
Public key cryptography depends on key pairs: one [private key] to be held by the owner and used for signing and decrypting and one public key that can be used for encrypting data sent to the public key owner or authenticating the certificate holder’s signed data. The digital certificate enables entities to share their public key so it can be authenticated.
Digital certificates are used in public key cryptography functions most commonly for initializing Secure Sockets Layer ([SSL] connections between web browsers and web servers. Digital certificates are also used for sharing keys used for public key encryption and authentication of digital signatures.
-
Most commonly for initializing Secure Sockets Layer ([SSL] connections between web browsers and web servers. or credit cards with chip, digital payments, validation for website domains
-
Certificate authorities ([CAs] considered trusted third parties in the context of a PKI – issue most digital certificates. Using a trusted third party to issue digital certificates enables individuals to extend their trust in the CA to the digital certificates it issues.
-
What is a digital certificate?
A digital certificate, also known as a public key certificate , is used to cryptographically link ownership of a public key with the entity that owns it. -
What is the difference between a digital certificate and a public key?
Digital certificates include the public key being certified, identifying information about the entity that owns the public key, metadata relating to the digital certificate and a digital signature -
What is the most common use case for digital certificates?
Used in SSL connections between web browsers and web servers -
What is a certificate authority?
But certificate authorities considered trusted third parties in the context of a PKI
-
What is a digital certificate?
A digital certificate is a digital document that verifies the ownership of a public key. It links the public key with the entity that owns it, ensuring secure communication and authentication. -
What is the difference between a digital certificate and a public key?
A public key is a part of a cryptographic key pair used for encrypting data. A digital certificate, on the other hand, includes the public key along with identifying information about the owner and a digital signature from a certificate authority to verify the key’s authenticity. -
What is the most common use case for digital certificates?
The most common use case for digital certificates is establishing Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) connections between web browsers and web servers to ensure secure and trusted online communications. -
What is a certificate authority?
A certificate authority (CA) is a trusted third party that issues digital certificates. The CA verifies the identity of the certificate holder and signs the certificate to confirm its authenticity.
-
What is a digital certificate?
A digital certificate is a digital document that verifies the ownership of a public key. It links the public key with the entity that owns it, ensuring secure communication and authentication. -
What is the difference between a digital certificate and a public key?
A public key is a part of a cryptographic key pair used for encrypting data. A digital certificate, on the other hand, includes the public key along with identifying information about the owner and a digital signature from a certificate authority to verify the key’s authenticity. -
What is the most common use case for digital certificates?
The most common use case for digital certificates is establishing Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) connections between web browsers and web servers to ensure secure and trusted online communications. -
What is a certificate authority?
A certificate authority (CA) is a trusted third party that issues digital certificates. The CA verifies the identity of the certificate holder and signs the certificate to confirm its authenticity.